Key Takeaways
- Firefighter and EMT training is crucial for a successful career in emergency services.
- Hands-on experience and comprehensive coursework are essential components of training programs.
- Certification and continuous education play significant roles in the career progression of firefighters and EMTs.
- Mental and physical preparedness is equally important in these demanding professions.
- Trained professionals are vital for community safety and emergency response efficiency.
The Importance of Comprehensive Training
Embarking on a career as a firefighter or EMT is a noble pursuit, requiring a blend of physical endurance and cognitive skills. Comprehensive training ensures these professionals can handle emergencies efficiently and safeguard lives. An emergency medical responder course Texas is an excellent pathway for those looking to advance their readiness. These training programs often comprise extensive coursework, which includes theoretical knowledge about fire science, emergency medical techniques, hazardous material handling, and disaster management.
Hands-on experience in realistic scenarios further solidifies this knowledge. Future firefighters and EMTs can develop their skills in a safe yet challenging environment by practicing in controlled settings. This dual theoretical and practical training approach equips trainees with the confidence and competence to handle real-life emergencies.
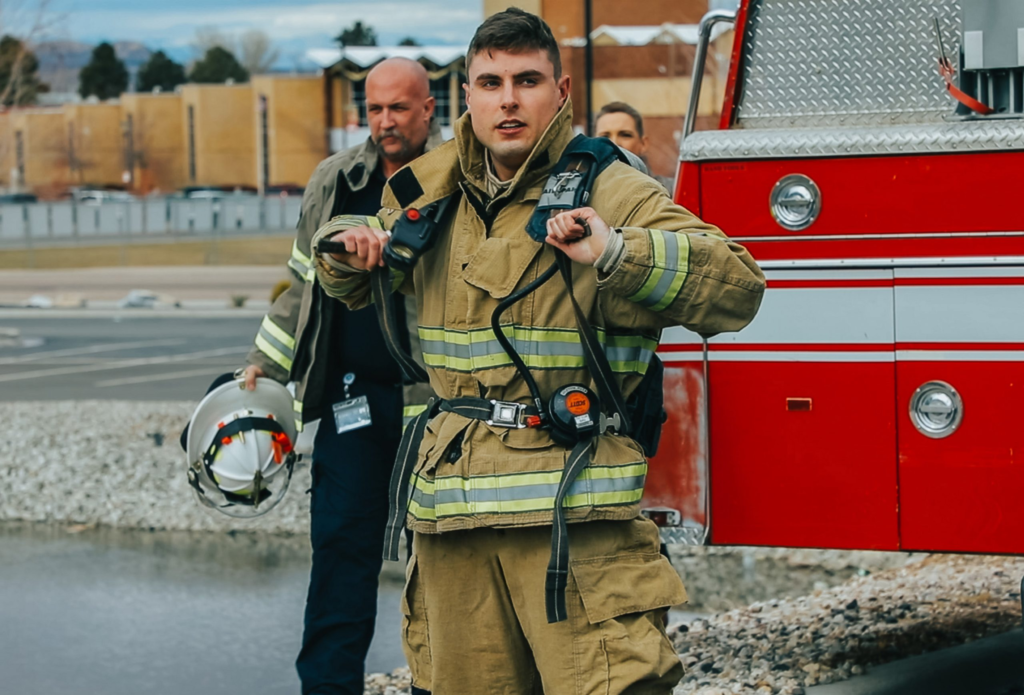

Hands-On Experience: Learning by Doing
One of the most critical components of firefighter and EMT training is hands-on experience. Real-world simulations and field exercises equip trainees with practical skills. For example, firefighting drills might include live fire scenarios, while EMT students might participate in mock medical emergencies. This hands-on approach is vital for building the confidence and competence required in real-life emergencies. The practical training also includes using firefighting equipment, emergency medical kits, and rescue tools, providing trainees with a feel for actual field conditions.
Moreover, collaborative exercises with local fire departments and emergency services enhance the learning experience by exposing trainees to real-world teamwork and communication dynamics. These interactions are invaluable as they mirror the inter-agency coordination necessary during actual emergency responses, ensuring that trainees are well-prepared for collaborative efforts.
Certification and Continuous Education
Obtaining the necessary certifications is a critical milestone in becoming a firefighter or EMT. These certifications, often mandated by state or national agencies, validate an individual’s proficiency and knowledge. For instance, certification courses might cover essential life support, advanced cardiac life support, and trauma response techniques. Moreover, ongoing education is essential because it keeps professionals updated on the newest methods and laws. According to the USFA National Fire Academy, ongoing training is essential for career advancement and ensuring high standards in emergency services.
Enrolling in advanced courses and attending workshops can significantly enhance a professional’s skill set and career prospects. Continuous education also involves adapting to technological changes, medical procedures, and fire safety protocols. This commitment to lifelong learning ensures that firefighters and EMTs can provide the best possible care and response when called upon.
Mental and Physical Preparedness
A career in emergency services is demanding both physically and mentally. Recruits must undergo rigorous physical training to meet the demands of the job. This encompasses fitness routines designed to enhance stamina, strength, and agility. Physical fitness goes beyond merely passing initial assessments; it requires sustaining a high fitness level throughout one’s career to meet the ongoing physical demands. Additionally, mental resilience is crucial. Professionals often witness distressing situations and need strategies to cope with the associated stress. Resources like the National Fallen Firefighters Foundation emphasize the significance of mental health support for firefighters and EMTs.
Counseling, peer support groups, and mental health training can help maintain mental well-being. Techniques such as stress management, mindfulness, and regular mental health check-ups are encouraged to ensure that professionals remain psychologically fit to perform their duties. Addressing the mental faculties is as essential as physical preparedness, ensuring overall professional well-being and longevity.

Role of Technology in Training
Contemporary technologies have transformed emergency service training. Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) simulations offer immersive training environments. These technologies enable trainees to experience various scenarios without the associated risks, enhancing their readiness for real-life situations. For instance, AR applications can simulate hazardous materials spills or multi-casualty incidents, providing valuable experience in a controlled and safe environment.
This integration of technology offers a more comprehensive and practical training approach. VR can replicate various emergencies, such as structural collapses or vehicle extrication, allowing trainees to practice their skills repeatedly without risk. Additionally, these tech-based solutions can provide instant feedback, helping trainees to correct and refine their techniques quickly. As technology advances, its incorporation into training programs will likely expand, offering even more sophisticated and realistic training opportunities.
Community Impact of Trained Professionals
The impact of well-trained firefighters and EMTs extends beyond individual emergencies. These professionals play a critical role in community safety and disaster response. They are often the first line of defense in various emergencies, providing essential aid and stabilization. Public education initiatives also help communities prepare for emergencies, reducing potential risks and improving safety.
Programs such as fire safety seminars, CPR training, and emergency preparedness workshops illustrate these professionals’ proactive role in fostering community resilience. By educating the public on fire prevention, first aid, and emergency response, they significantly reduce the incidence and impact of emergencies. This educational role further enhances community trust and cooperation, vital during large-scale emergency responses.